You must have encountered the term critical path analysis or method in management school. Most management students and trainees are unsure about this project management tool until they assume the role of a project manager. Since you will manage a real-world business project, you must understand CPM and its importance. Otherwise, your project may suffer timing and deliverables issues. Continue reading this post on CPM to acquire a clear and actionable understanding of the critical path analysis. You will also learn about some linked aspects of CPM that will help you in the business world.
What Is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
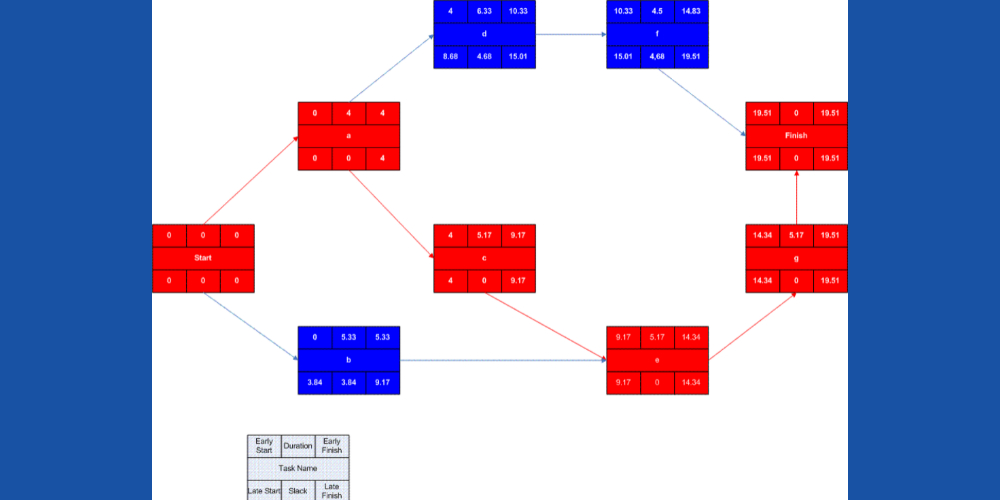
The critical path method is a process where a project lead identifies vital tasks that help complete the project on time. Thereby, it becomes easier to determine task scheduling. It is the series of tasks that constitute the longest time span. You must finish these tasks on time to ensure the whole project completes as per the schedule. If you see any delay in executing the critical tasks, the entire project will also get delayed. CPM analysis primarily revolves around identifying task dependencies, finding out the most critical tasks of the project timeline, and computing the duration of the tasks. The technique has been a powerful project management tool for more than 60 years since its inception in the late 1950s. It was mainly created to address the increased project cost issues due to inept task scheduling. Now, it is the tool of the choice for task prioritization or project planning.
The Major Components of CPM Analysis
There is a standardized approach to critical path analysis so that project managers and stakeholders across countries and industries can understand the CPM network of any project. To create a standard CPM format, you must include the following components:
The Earliest Start Time (ES)
It simply indicates the earliest timestamp within the project when your team can start working on any task. However, you need to know task dependencies and subtasks to compute the ES.
The Latest Start Time (LS)
On the contrary, the LS is the very last minute when your team can start working on a particular task. If the team overshoots the LS value, then there is a possibility of project delay.
The Earliest Finish Time (EF)
This figure indicates the earliest timestamp on a project timeline when your team can complete a task. You can derive the value by taking into account the earliest start time and task duration.
The Latest Finish Time (LF)
LS value tells you how much delay a task can absorb before completion that will not affect the whole project completion time frame. This value also depends on the latest start time and task duration.
Float
Float is also known as slack. It informs you how long your team can delay a task before such task deferment impacts the network of subsequent tasks and project schedule. You must maintain zero floats for the critical path tasks.
The Critical Path Method Algorithm
The critical path algorithm defines how the network of tasks will take shape. It primarily has two parts:
Forward Pass
The forward pass deals with values like the earliest start time (ES) and the earliest finish time (EF). It uses a network diagram of tasks and an estimated time span for each activity to compute the ES and EF of the critical tasks. The ES of any task will always be equal to the EF of its precursor activity. The EF calculation formula is: At the end of the network diagram, you should see the EF of the last task of your project. This time, date, or day value is equivalent to the time span of the entire project.
Backward Pass
The backward pass lets you determine late finish and late start values for any project tasks. Thus, you can compute the project time span and finally identify the critical path. Here, the LF is the last task’s EF. The calculation formula that you can use is: This algorithm also lets you calculate LF for preceding tasks of the last task. For this purpose, LF will be the ES of the task that immediately follows.
How to Find the Critical Path Using CPM
#1. Gather all the project tasks in a table. You can use a work breakdown structure for this purpose. From the start to the final deliverable, ensure every task are there. #2. Through collaborative brainstorming, identify task dependencies. Dependent tasks are those activities that can not begin until you complete a preceding task. #3. Now, construct a network diagram of tasks according to their order of appearance. You can also call it the CPM chart. #4. Once you have created the CPM chart, it is time to estimate the time span for each task. You can take help from subject matter experts, old projects, etc., to allocate time to all the project activities. #5. You can now use the CPM algorithm to calculate values for ES, EF, LS, and LF of activities in the project. #6. You should now compute the float for each task. You can simply subtract ES from LS to find the float value. #7. The network of tasks with zero floats constructs the critical path. All these tasks are dependent except for the first task of the CPM chart. #8. You can keep updating the CPM chart as you start executing the project.
How to Calculate Project Length Using CPM
#1. Mention the start time and end time of each project task in the network diagram. #2. The start time of the first task is 0, and the end time of that task is simply the task duration. #3. Similarly, the start time of the next activity is the end time of its predecessor. The end time is, however, the sum of task duration and start time. #4. Follow the above until you compute the start time and end time of all the tasks within the CPM chart network. #5. The end time of the last task in the critical path series is the end time of the entire project.
The Use Cases of Critical Path Analysis
Calculate Task Float
You can use the CPM chart to compute the float of tasks. A zero float means the project tasks are set in place, whereas a positive float indicates the project activities are flexible. Non-critical tasks could have a higher float value.
Compressing Schedules
If you need to complete a project before the scheduled deadline, you can use compression techniques like fast-tracking and crashing tasks. A CPM chart will help you determine which tasks are eligible for fast-tracking.
Data for Future Use
A CPM chart gets updated as the project progresses. You can compare the CPM chart of any project in different phases to make a more accurate time estimation of future projects.
Advantages of Critical Path Method
#1. The primary benefit of the CPM analysis is the efficient scheduling of project tasks. The process clearly segregates non-critical tasks from critical ones. Thus, you can assign critical activities to highly-experienced employees and non-critical tasks to employees with lesser experience. #2. You get an estimated project completion time and individual time span for tasks and subtasks. You can enter these in a project management tool for task status monitoring. #3. You can allocate more human resources to lengthy and critical tasks as they get freed from non-critical tasks. #4. Project cost budgeting is a challenging task for project managers. But, with the CPM analysis, you can break the budget into small parts and assign them to tasks and subtasks for easier project budgeting.
CPM Analysis Tools
Though you can use a pen and paper to draw a physical CPM network or use Microsoft Visio to draw the same, it will become too manual and a hectic process. Instead, you can automate the entire CPM analysis procedure using any of the following tools:
Critical Path Method Analysis on Smartsheet
Smartsheet is a renowned work collaboration and management tool in a spreadsheet-like user interface (UI). It provides many project management templates, so you do not need to create one from scratch. One such helpful template is a Gantt chart template formatted especially for CPM analysis. To establish the project’s critical path, use the Basic Project with Gantt & Dependencies template. Open it and enter project tasks in the Section column header. If there are any subtasks, you can also type in those tasks. Now, just add the Start and End date or time of the tasks. You may also need to establish task dependencies, if any. You can now click on the Show Critical Path option on the top-right corner of the Gantt view to change it to CPM.
Lucidchart as a CPM Software
Lucidchart is a leading diagramming app on the cloud that lets you combine project collaboration, data visualization, and workflow diagramming in one centralized software. Since the app is accessible from anywhere via the internet and a web browser, you can increase the team’s understanding of the project and drive productivity. It comes with various diagramming templates for CPM analysis. You can simply choose one from the library and personalize it. You can add formulas in flow chart shapes to automate the project duration planning through CPM. Furthermore, Lucidchart offers various integration options to edit, access, and share the CPM directly to business apps like Salesforce, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, etc.
Critical Path Software From ProjectManager.com
ProjectManager is a full-service project management application based on cloud computing. You can compute the critical path of any project using the Gantt chart feature of this tool. Using the tool is pretty simple for CPM analysis. All you need to do is submit some project details like tasks, subtasks, start date, end date, and dependencies. The application will automatically create a project timeline. Now, simply change the view filter to the critical path and find which tasks require your immediate attention.
Critical Path Software From Creately
Creately is yet another popular diagramming tool also suited for professional CPM analysis. You can use various shapes on this tool to structure your own critical path network. It comes with drag and drop functionality so that you can quickly create a network of tasks for critical path determination. Furthermore, Creately’s artboard has an infinite canvas. Thus, if your project is highly complex and large, you can still use this tool. Moreover, sharing a CPM workspace is quite easy through link-sharing or collaborator invitations. Thus, you can discover the critical tasks of a project while working together with your project team online.
Final Words
The critical path method is a mighty tool that all project managers must learn to manage project resources, time span, and tasks efficiently. You can create project tasks’ schedules and assign them to the project team members with the help of this tool. It also lets you efficiently track the tasks’ statuses and the overall project progress. Moreover, this tool is highly important for project leads and managers working concurrently on complex and multiple projects. Ultimately, CPM enables you to concentrate your efforts on professional task optimization and handle the project efficiently without missing any project milestones.